Synthesis of cyclic polymers for biomedical applications
Internship
Type of Project: Experimental
Location: Donostia
Supervisor:
Fabienne Barroso-Bujans (webpage)
fbarroso@ehu.eus
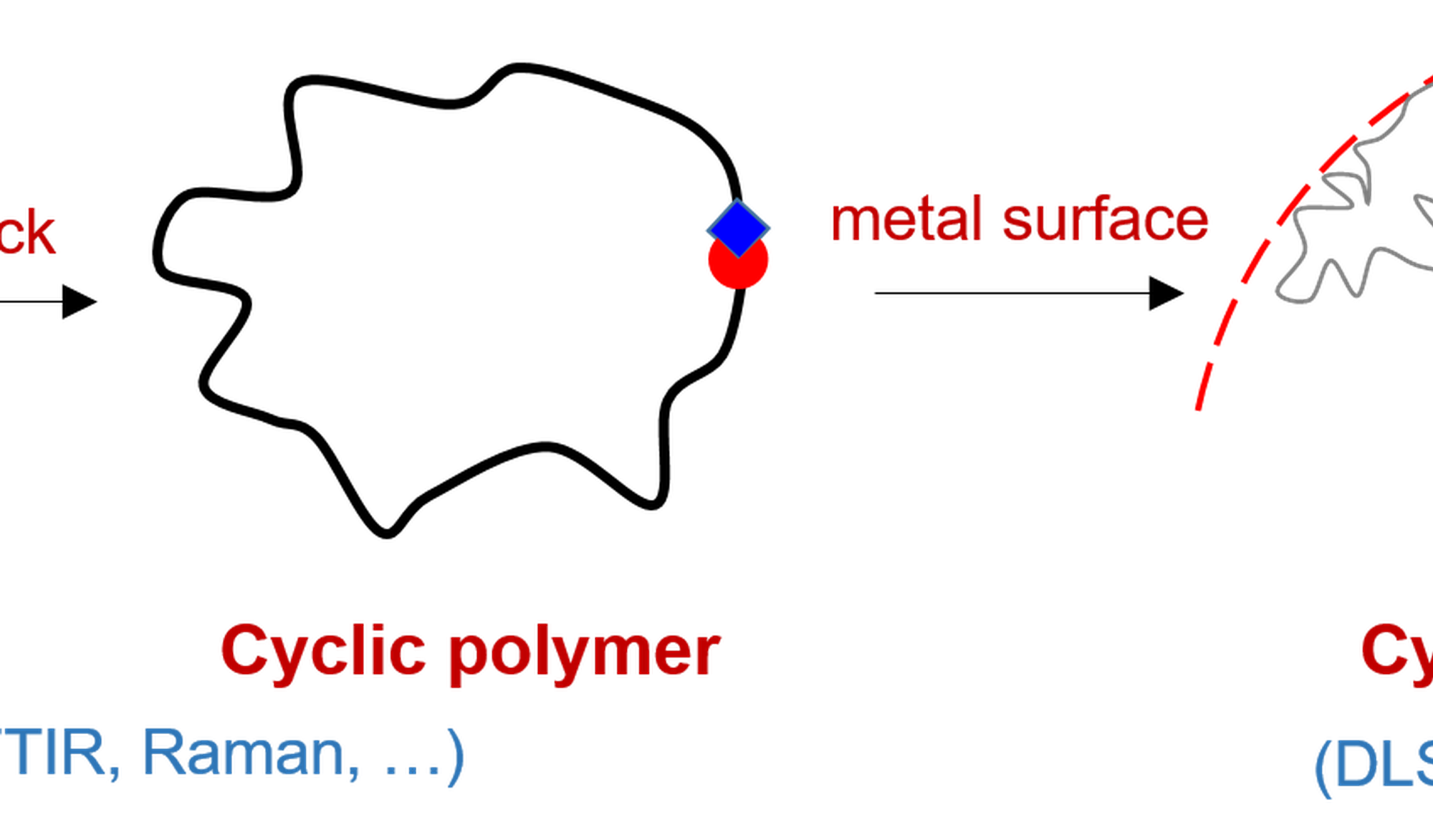
Cyclic polymers possess unique physico-chemical properties compared to their linear counterparts as a result of the absence of end-groups and the equivalence of all monomer units. These differences may be expressed in their distinct hydrodynamic, rheological, optical and thermal properties. Nature has already taken full advantage of the unique properties of cyclic biomacromolecules. For example, circular DNA is ubiquitous and shows increased resistance to enzymatic degradation. Understanding and taking full advantage of the unique character of cyclic polymers require a synergistic effort between the advances in their synthesis and the progress in their physico-chemical characterization.
In this project the student will explore new approaches to synthesize hybrid materials composed by cyclic polymers and a metal with potential applications in biomedicine. The student will learn to use synthesis techniques for producing cyclic polymers, including ring closure approaches combined with click-chemistry reactions. In addition, the student will benefit from the opportunity to work on state of the art instruments for polymer chemistry. Some of them include GPC with triple detection, MALDI-TOF MS, NMR, FTIR and Raman spectroscopy.
